Medical AI
Medical AI involves the application of artificial intelligence technologies to healthcare, aiding in tasks such as diagnostics, treatment recommendations, and patient monitoring. It enhances the accuracy and efficiency of medical processes, reducing the workload of healthcare professionals and improving patient outcomes across various medical fields.
We design different frameworks for various medical tasks such as retinal disease diagnosis.
Highlight
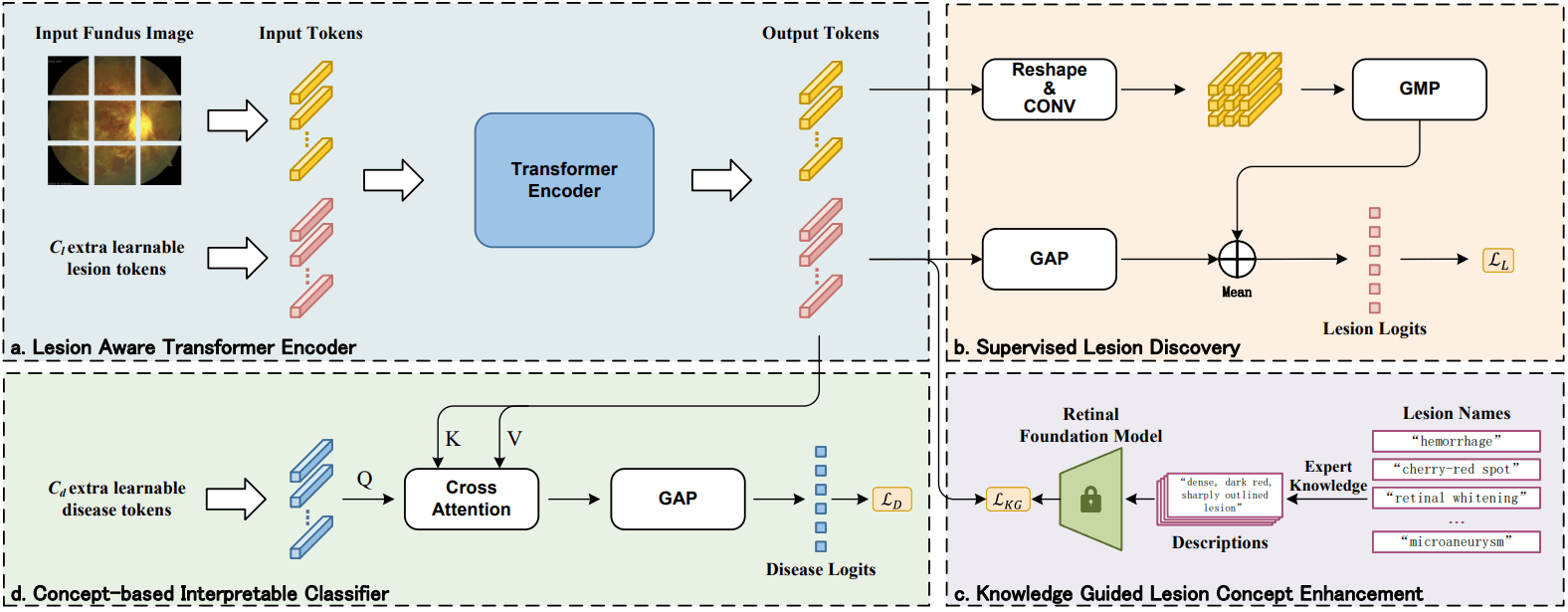
Concept-based Lesion Aware Transformer for Interpretable Retinal
Disease Diagnosis
IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging (TMI), 2024.
We regard retinal lesions as concepts and propose an inherently interpretable framework designed to enhance both the performance and explainability of diagnostic models. Leveraging the transformer architecture, known for its proficiency in capturing long-range dependencies, our model can effectively identify lesion features. By integrating with image-level annotations, it achieves the alignment of lesion concepts with human cognition under the guidance of a retinal foundation model. Furthermore, to attain interpretability without losing lesion-specific information, our method employs a classifier built on a cross-attention mechanism for disease diagnosis and explanation, where explanations are grounded in the contributions of human-understandable lesion concepts and their visual localization.
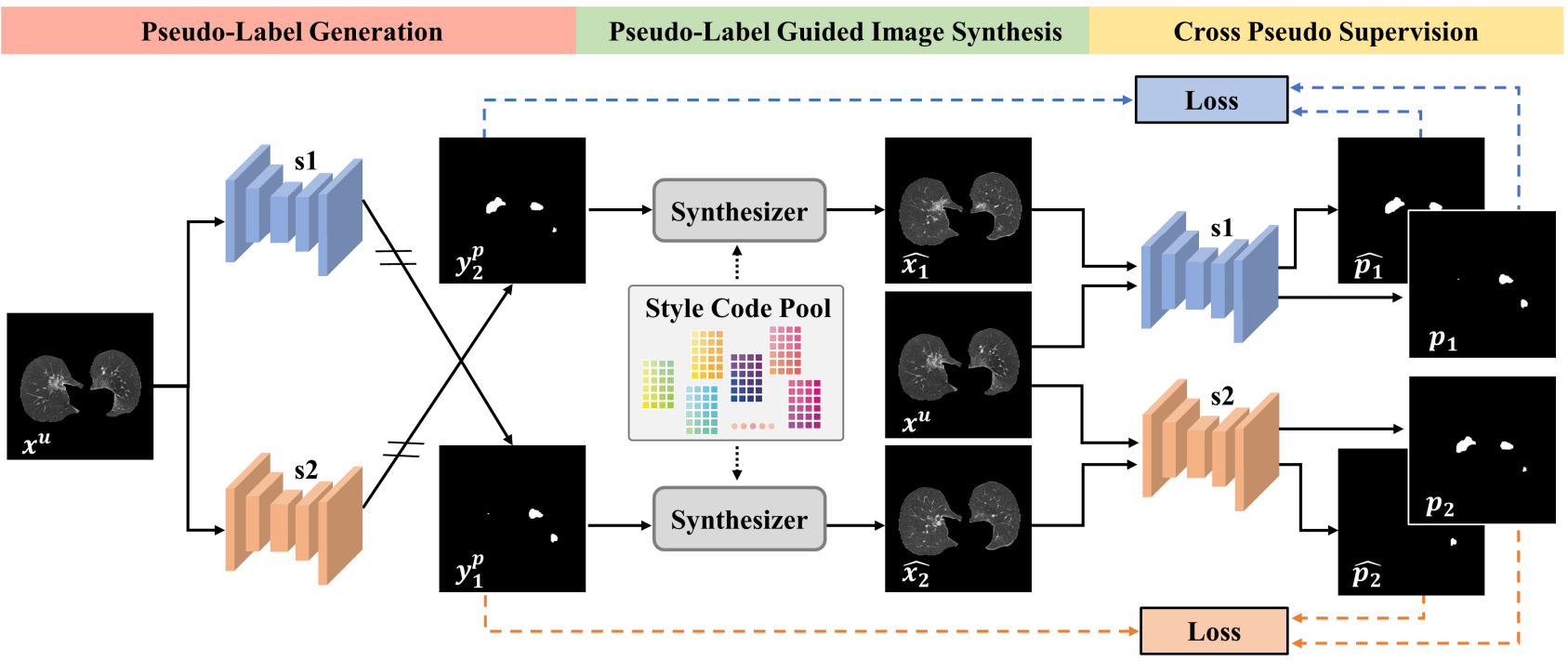
Pseudo-Label Guided Image Synthesis for Semi-Supervised COVID-19
Pneumonia Infection Segmentation
IEEE Transactions on Medical Imaging (TMI), 2022.
We propose a new perspective on semi-supervised learning for COVID-19 pneumonia infection segmentation, namely pseudo-label guided image synthesis. The main idea is to keep the pseudo-labels and synthesize new images to match them. The synthetic image has the same COVID-19 infection regions as indicated in the pseudo-label, and the reference style extracted from the style code pool is added to make it more realistic.